Reinforcement Learning
Sequential decision making and credit assignment under uncertainty and partial observability is central to developing Intelligent Systems. Reinforcement Learning (RL) provides a general and powerful computational framework for sequential decision making. It involves an agent interacting with the environment to maximize a reward function by selecting actions.
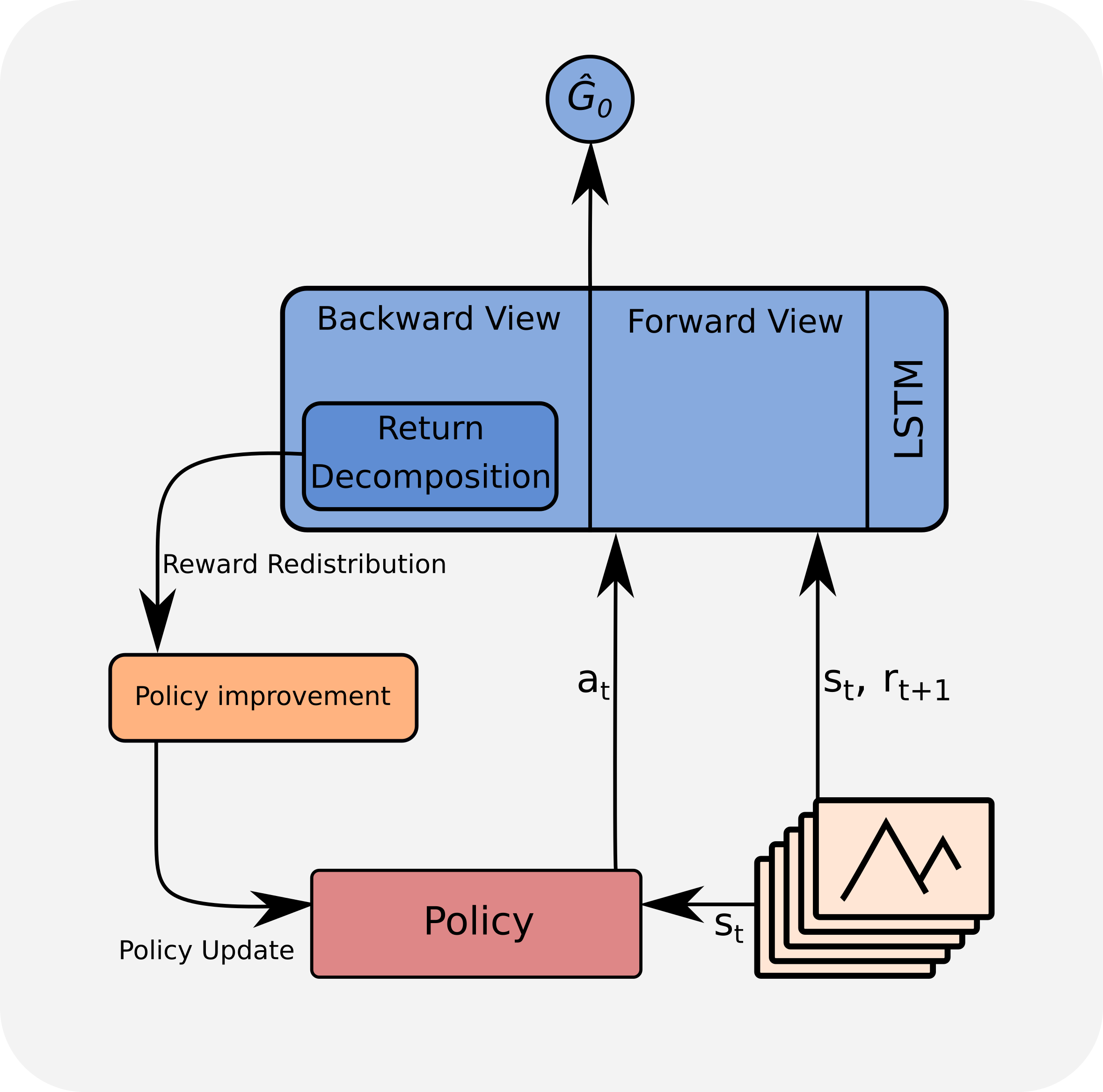
Our research at the Institute of Machine Learning focuses on developing new algorithms and theory required to improve the state of the art in Reinforcement Learning. Credit assignment under delayed reward has been central to our work in recent years. We also actively pursue developing new function approximation methods for scaling Reinforcement Learning to high dimensional problems. Learning to take decisions based on stored data is another area of interest. We actively apply Reinforcement Learning to various applications including robotics, logistics, natural language processing and others.
recent publications in Reinforcement Learning:
- arXivConvergence Proof for Actor-Critic Methods Applied to PPO and RUDDER2020